HowTo: Keep your processes running continuously
- When we operate containers using SSH, the processing might be interrupted due to the Internet disconnection. We provide the following 3 solutions to ensure that the computing work can continuously run in the background.
Method 1. Using Jupyter Notebook
Step 1. Click into the created Interactive Container in TWSC
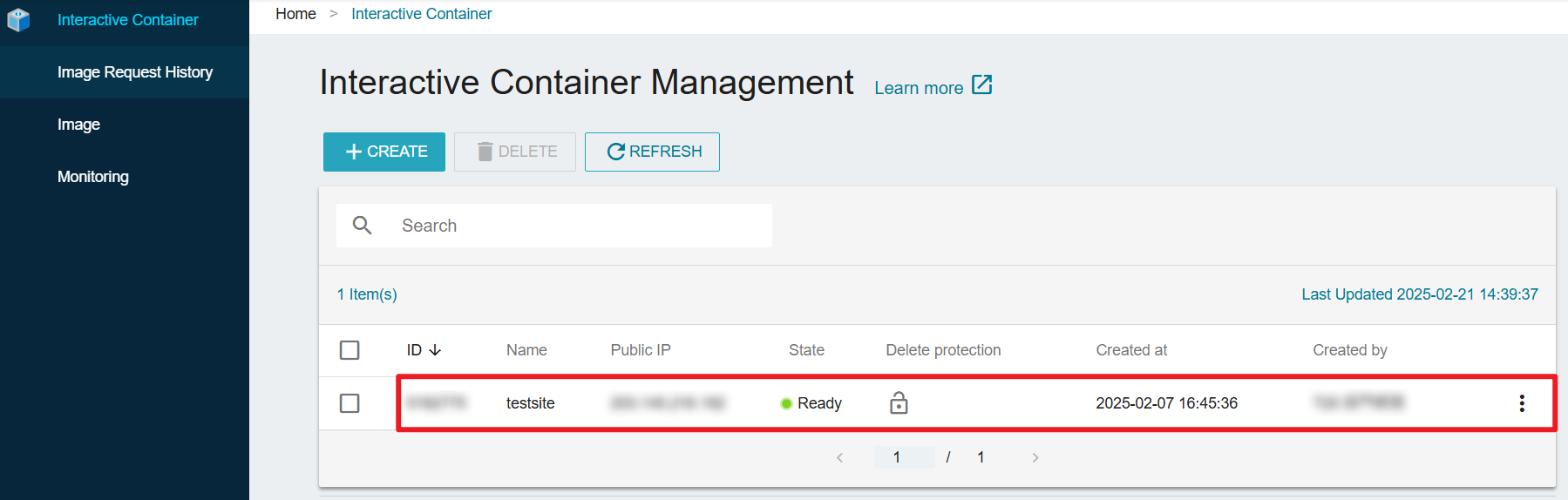
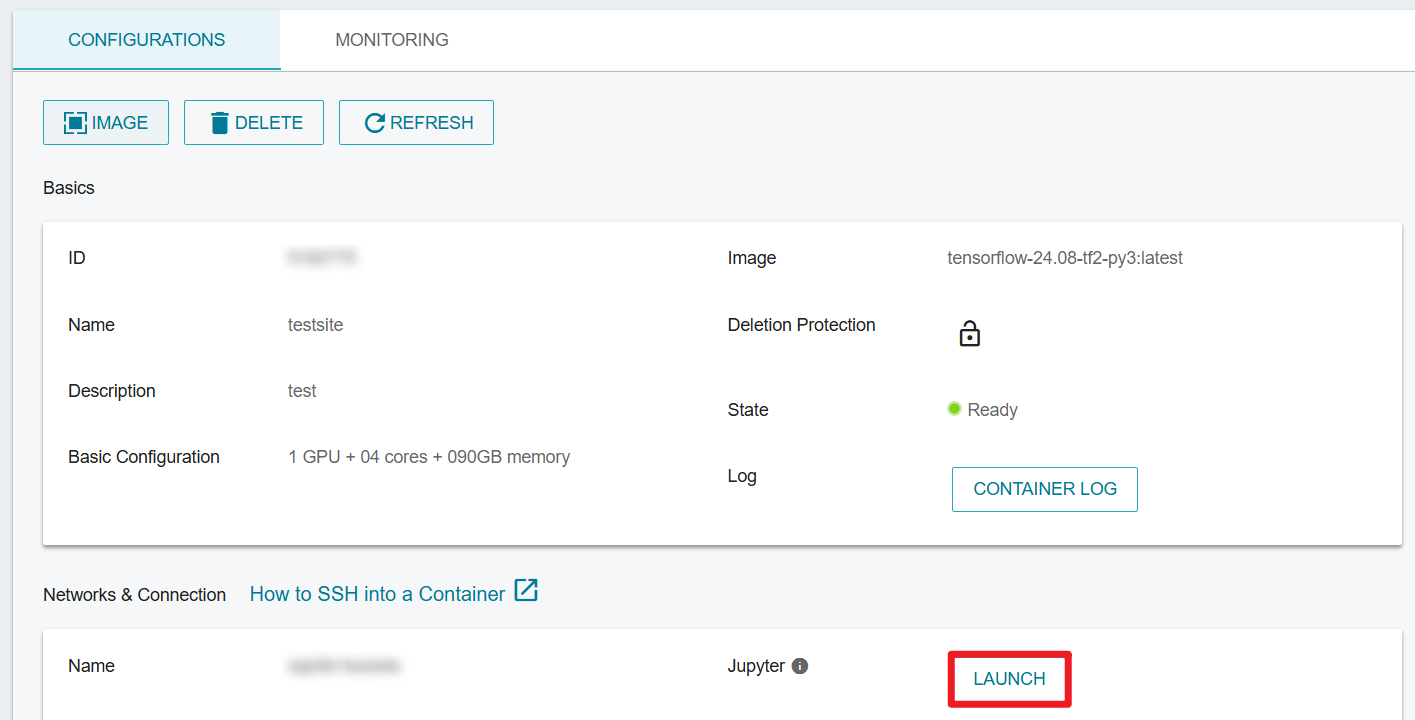
Step 2. Connect to the the container using Jupyter Notebook
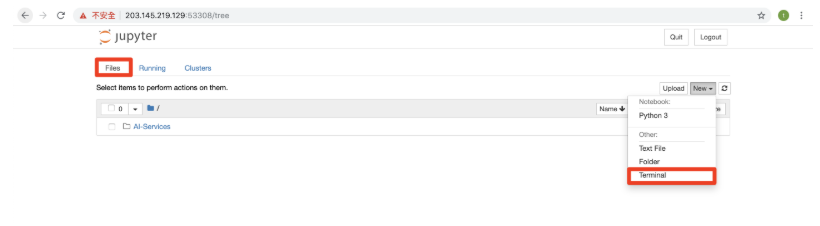
Step 3. Open the terminal to operate the container
Step 4. Enter and run the command
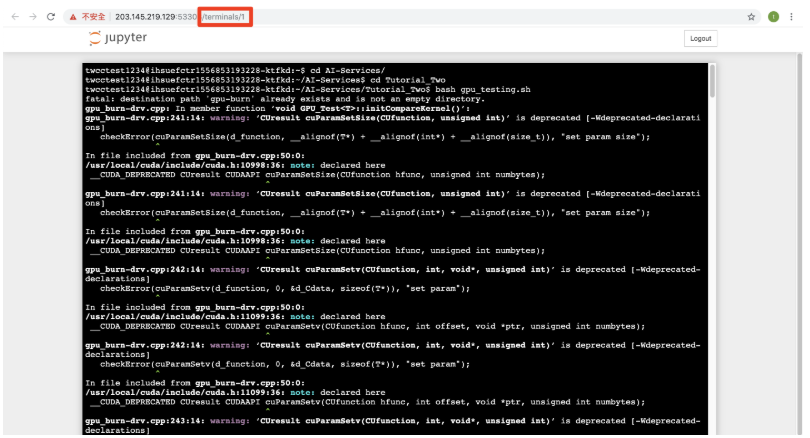
info
💡 The URL bar will display the terminal number: terminals/1, which will be used for the following steps.
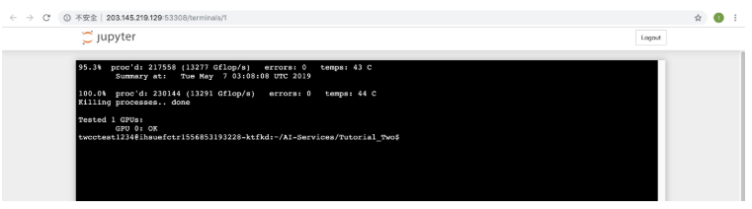
Step 5. Check the status of the running process
- If you close the Terminal, the process will run continuously in the background.
- To check the running status of the process, click Running in Jupyter Notebook, and click the terminal number you want to check below.

- Then you are able to enter Terminal again to check the status of the running process.
Method 2. Using Screen
Step 1. Install Screen
- Connect to the container using SSH, and then enter the command to install Screen:
sudo apt-get install screen
info
Please refer to Connect to the container using SSH.
info
⚠️ Warning: If the installation process shows E: Unable to locate package screen, please run the following command to update, then install Screen again.
sudo apt-get update
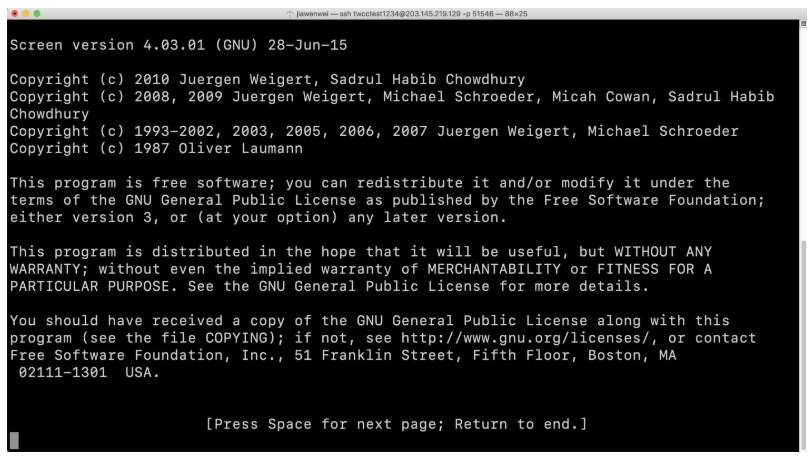
Step 2. Enter Screen
screen
- After entering Screen, please read the description.
- Press Return key to enter the command
Step 3. Run the process in the screen shell
- The example is as follows:
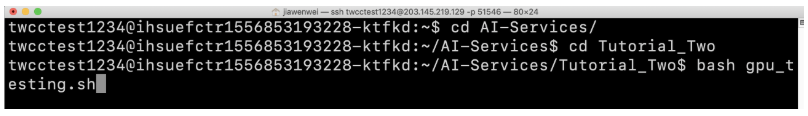
Step 4. Detach screen shell
- When the process is running, press
ctrl + a + d, it will show detach successful message (shell ID marked with red frame). Then, the process can run continously in the background, even if SSH is disconnected.

Step 5. Check the status of the running process
- If you want to enter that screen shell again, enter the command to operate container and check the status of the process:
screen -r [A chunk of screen shell ID]
Method 3. Using Linux nohup command
Step 1. Connect to the container using SSH and run the process
- Enter the command below to run the process in the background.
nohup [/code_path] &
info
Please refer to Connect to a container using SSH.
- The example is as follows, terminal will return the job ID (job ID = 1 marked with red frame), and the output of the process will be displayed in the "nohup.out".
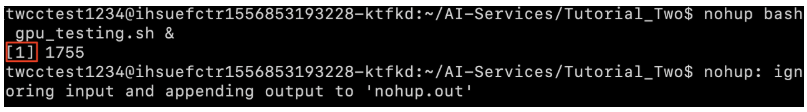
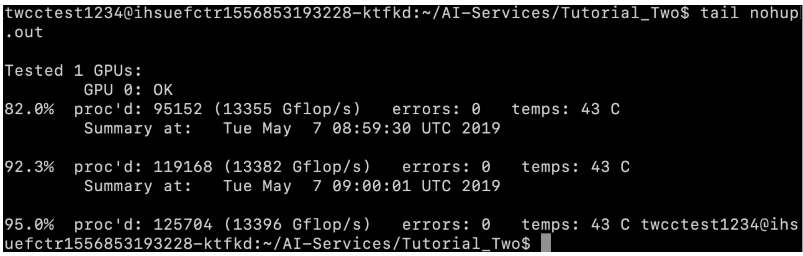
Step 2. View the output content
- Enter the following command to view the latest output of the process.
tail nohup.out
- The output is displayed as follows: