HowTo: Configure the service ports of an interactive container
TWSC Container Conputer Service adopts Port-Forwarding to forward external network connections to different containers under the same domain, so that users can use specified container services from external network.
SSH runs on port 22; Jupyter Notebook runs on port 8888. Besides, the container service opens external port: 5000, 5001 and 5002. You can set the daemon of the container service to one of the external ports, and associate the external port with the target port in Interactive Container Details page. After that, you can use the service from your local using the public IP and the external port.
The following demonstrates how to set up a web service with Flask in a container, set the daemon of the service on the external port 5002, and associate the service port to use the web service through a local browser:
Create a container
- After the container is created, open Jupyter Notebook ➡️ Terminal
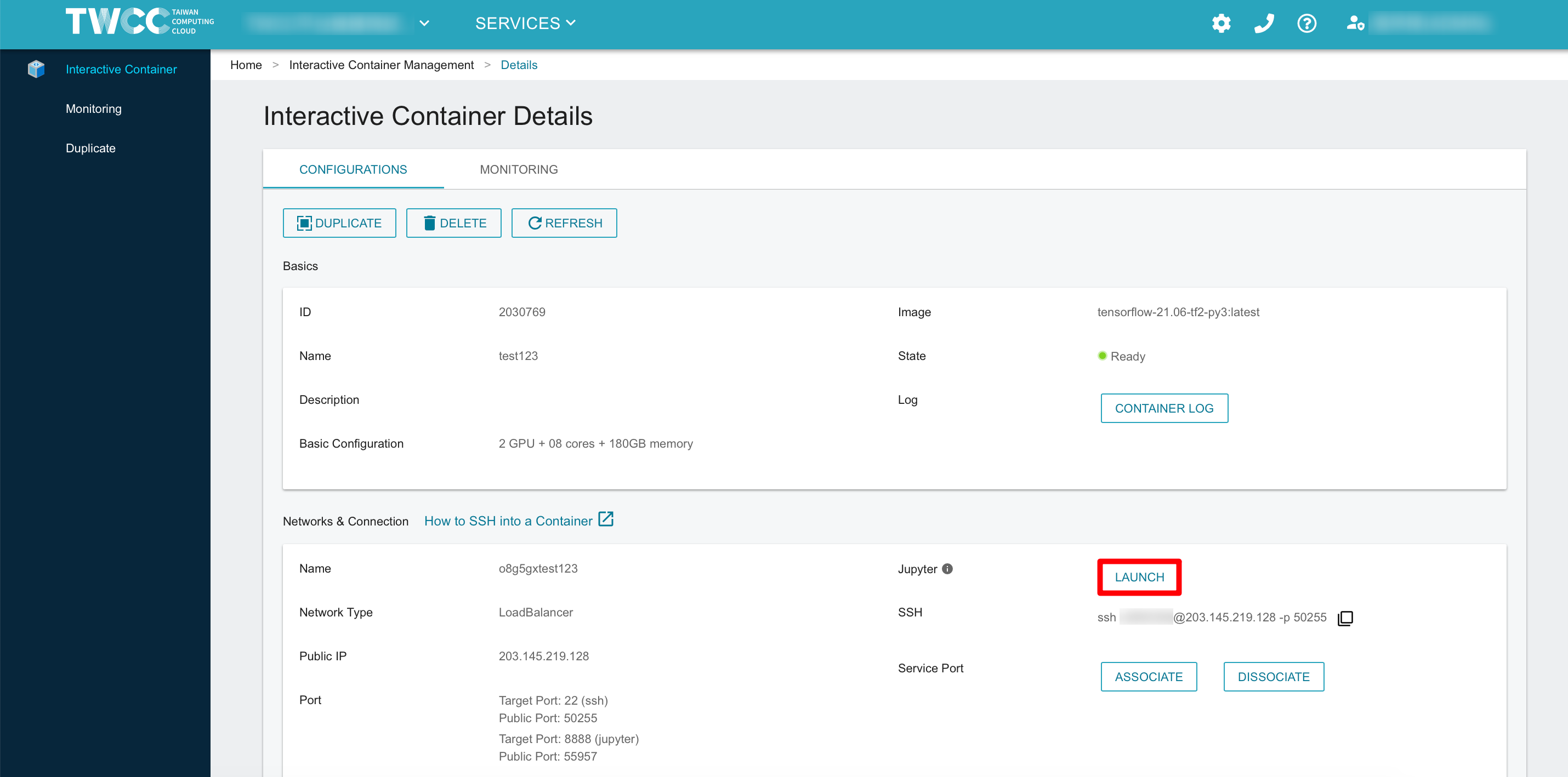
Configure a web service and a service port
- Enter the following command, download and run the script (script commands: install Flask to set up the website, make it display
Hello World, and set the port number to5002) to configure the web service using the container.
wget -O - https://gist.githubusercontent.com/geniusshiun/c9e424e388e5cc7db3f73bf67916e766/raw/cb5e34c832750763c19b1237755eac440101e809/gistfile1.txt | bash

- Make sure that the web service has been set up and the daemon is running on port
5002

Associate service ports
- Back to Interactive Container Details page, click ASSOCIATE➡️ select the port number of the service daemon
5002➡️ click OK
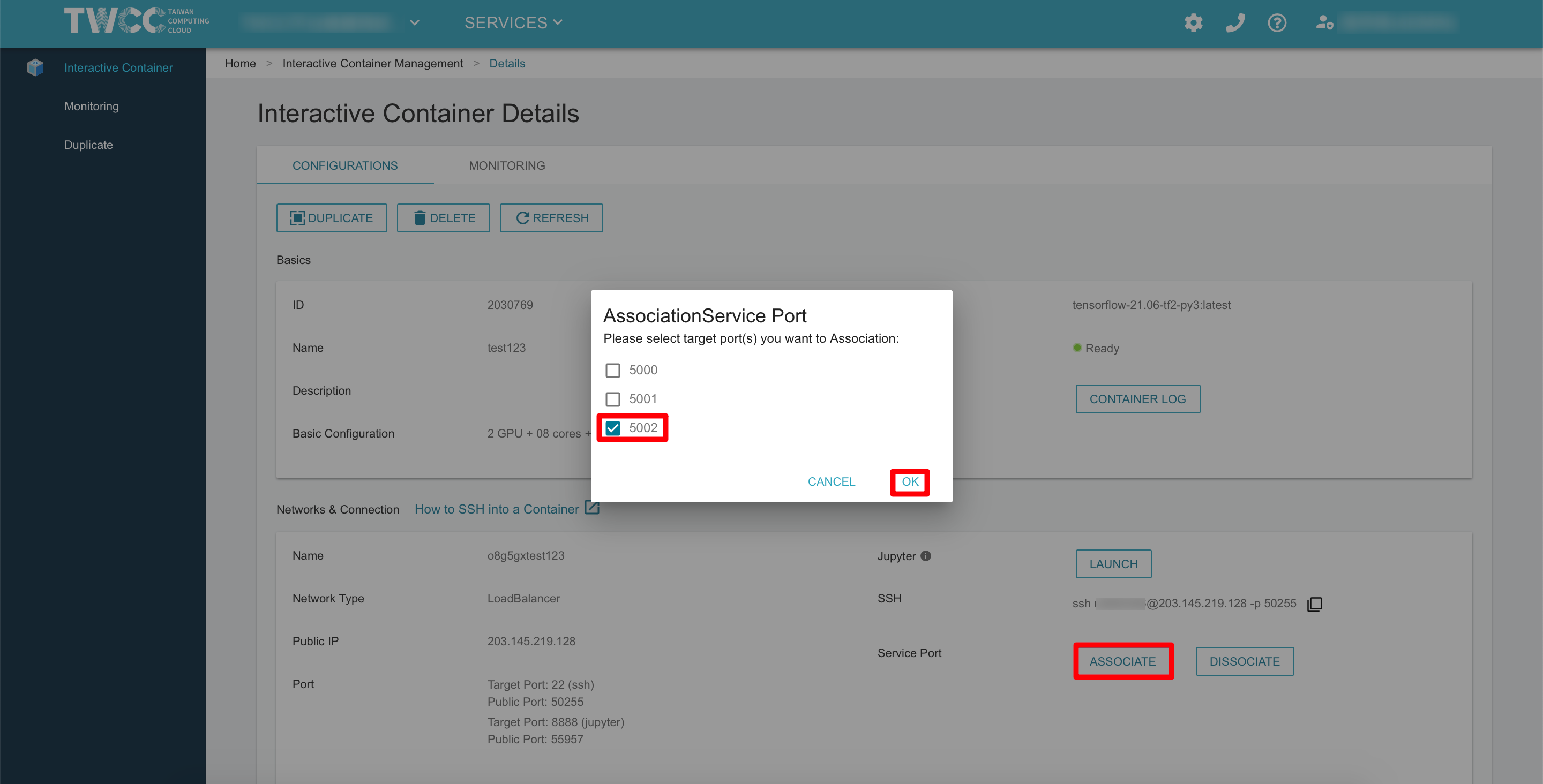
- After that, the system will allocate a target port (53055) corresponding to the external port (5002)
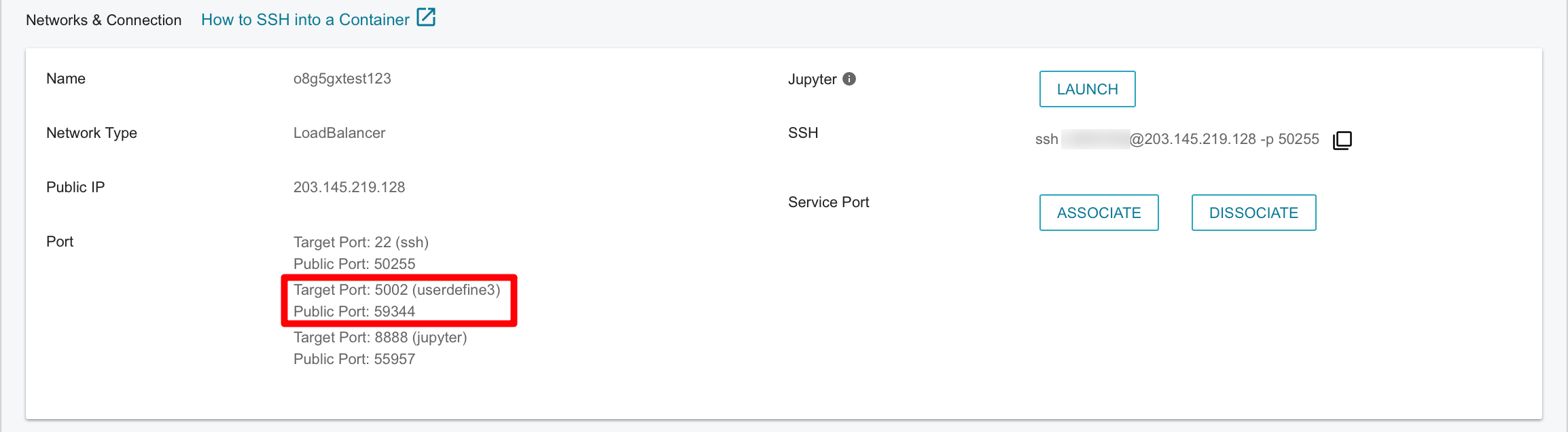
Use the web service
- Open your local browser and enter
http://public IP:target port number, then you can see the web page and start using the web service.
