Using Kubernetes Ingress
The Virtual K8s Service will automatically install the Ingress-Nginx Controller upon creation. For detailed information about the Ingress-Nginx Controller, please refer to this document. This article will introduce how to set up and use Kubernetes Ingress.
Before Getting Started
- Please see this document to create and access your cluster.
Steps to use Kubernetes Ingress
The steps to use Kubernetes Ingress are generally as follows, with a more detailed explanation of each step below.
- Step 1. Create a pod to provide backend server services.
- Step 2. Create a load balancer to provide an external endpoint for the backend server services.
- Step 3. Create an ingress to provide cluster routing and forwarding functionality, ensuring that HTTP requests are correctly routed to the backend server services.
Step 1. Create a pod
- Create an echo server and corresponding Kubernetes service.
vim echoserver.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: echo-server
namespace: ingress-test
labels:
app: echo-server
spec:
containers:
- name: echo-server
image: gcr.io/google-containers/echoserver:1.10
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: echo-server-service
namespace: ingress-test
spec:
selector:
app: echo-server
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 2145
targetPort: 8080
The above example is created under the "ingress-test" namespace. If the namespace has not been created yet, you can refer to the following steps to create the namespace.
vim ingresstest.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: ingress-test
- Apply the settings.
kubectl apply -f ingresstest.yaml
- Verify that the namespace has been created.
kubectl get ns
- Apply the settings.
kubectl apply -f echoserver.yaml
Verification.
- Verify that the pod has been created.
kubectl get po -n ingress-test
- Enter pod.
kubectl exec -it -n ingress-test <pod_name> -- bash- Use curl to verify if the service is running properly.
curl localhost:8080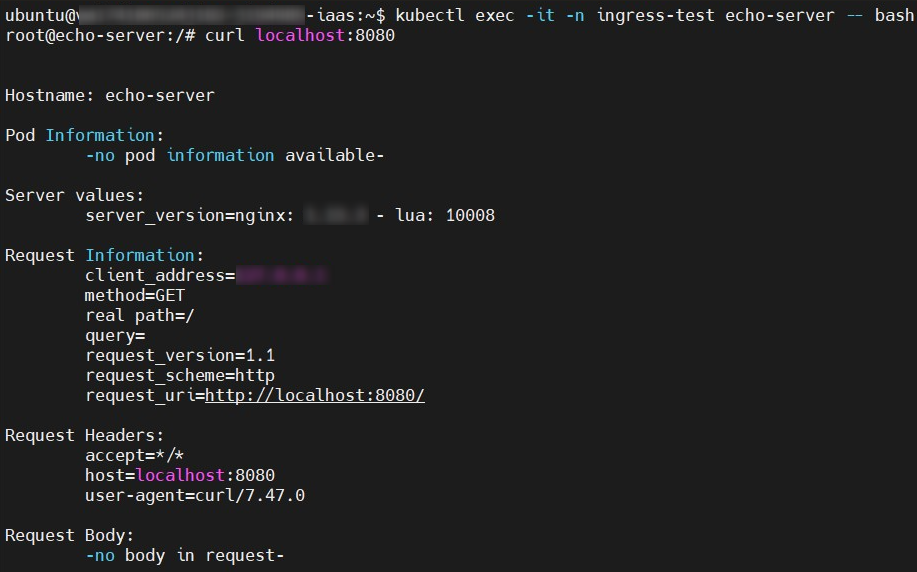
- If using another pod, you can connect via the cluster IP on port 2145.
kubectl get svc -n ingress-testcurl <cluster_ip>:2145
Step 2. Create a load balancer
This step is used to provide the external IP for the above echo server, allowing external users to connect to the echo server via this IP.
Note that the namespace of this load balancer must be ingress-nginx. Additionally, you can configure the IP whitelist using spec.loadBalancerSourceRanges to restrict access to specific IP ranges.
vim ingress-svc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/component: controller
name: loadbalancer-ingress-nginx
namespace: ingress-nginx
#annotations:
#loadbalancer.openstack.org/proxy-protocol: "true"
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
# 以下可限制來源IP白名單,以下範例僅允許10.96.150.0 - 10.96.150.255範圍的IP進入
# loadBalancerSourceRanges:
# - 10.96.150.0/24
externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: http
- name: https
port: 443
protocol: TCP
targetPort: https
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
- Apply the settings.
kubectl apply -f ingress-svc.yaml
- Verification.
kubectl get svc -n ingress-nginx

Step 3. Create an Ingress
- Create an ingress and configure the corresponding URL or path. The following example forwards any request with the path
/vkstestpathto the echo server.
vim ingress.yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: echo-ingress
namespace: ingress-test
# 以下可使用Ingress功能進行來源IP白名單
# annotations:
# nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/whitelist-source-range: 140.110.154.116/32
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /vkstestpath
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: echo-server-service
port:
number: 2145
- Apply the settings.
kubectl apply -f ingress.yaml
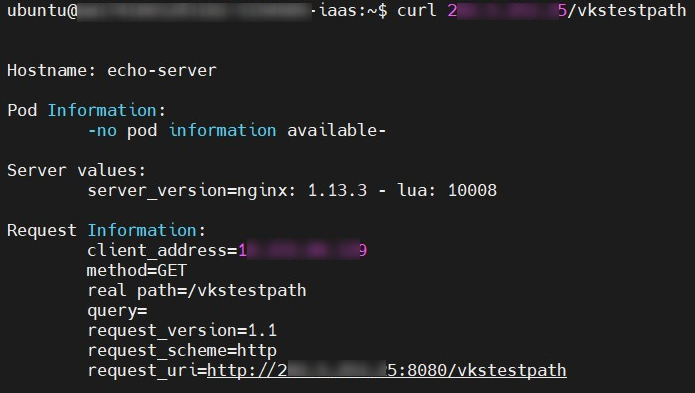
- To verify the configuration, you can use curl from outside the Kubernetes cluster to access the echo server through the l load balancer IP and the specified path (
/vkstestpath).
curl <loadbalancer_ip>/vkstestpath